Rising energy prices and climate change mean that more and more attention is paid to energy efficiency in construction. Energy-efficient houses not only contribute to reducing the negative impact on the environment, but also offer significant financial savings for their residents. In our text, we will look at the characteristics of energy-efficient houses, including passive houses, and what technologies and building materials enable achieving high energy efficiency.
Passive houses
Passive houses represent the highest thermal insulation parameters of all residential buildings. Designed to minimize energy demand for heating and cooling, they use the best insulating materials, air tightness and air recuperation. The key requirement for a passive house is to maintain a constant, comfortable temperature inside, with very low energy consumption. The benefits of living in such a house include not only lower energy bills, but also better indoor air quality.
Energy-saving houses
Different from passive houses, energy-efficient houses are designed to reduce energy demand, but without such stringent requirements. Key aspects such as good insulation, energy-efficient heating and ventilation systems, as well as intelligent energy management are the foundation for achieving energy efficiency in these buildings. These houses use traditional energy sources, but they do it much more efficiently than standard buildings. Investing in energy-saving technologies such as heat pumps, photovoltaic systems and LED lighting translates into long-term savings for owners.
Heat transfer coefficient
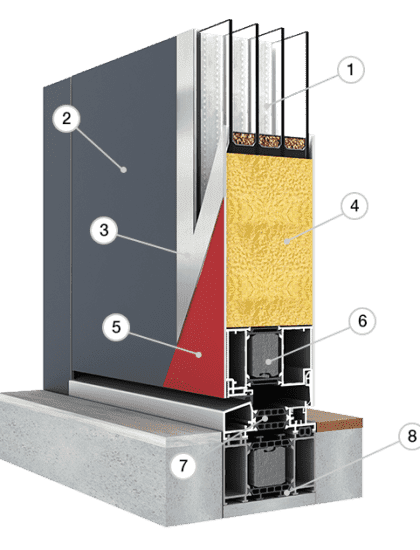
The heat transfer coefficient (U) is a measure that determines how well a building element (e.g. wall, window) insulates against heat loss. The lower the coefficient, the better the insulation and the lower the energy loss. Effective thermal insulation is crucial to ensuring high energy efficiency of the house, because it allows for a significant reduction in heating demand. Materials with a low heat transfer coefficient, such as polyurethane foams, mineral wool or special window systems, are widely used in energy-saving construction.

Energy-saving joinery
Windows and doors are one of the main sources of heat loss in your home. Energy-saving joinery, characterized by a low heat transfer coefficient, allows for a significant reduction in energy losses. Modern energy-saving windows are usually designed with large-chamber profiles with thermal breaks and triple glazing filled with noble gas (e.g. argon), which significantly improves their insulation. Choosing the right windows and doors is crucial to ensuring thermal comfort and reducing the costs of heating your home. DAKO's offer includes energy-saving joinery made of wood, PVC and aluminum.
The impact of solar energy on reducing heat demand
Using solar energy is one of the most effective ways to reduce the energy demand needed to heat the interior of your home. Photovoltaic panels and solar collectors allow you to directly obtain energy from the sun and use it to produce hot water, heating and even electricity. Integrating solar systems into an energy-efficient house can significantly reduce energy bills and increase the building's energy independence. The sun's rays, thanks to the large glazing in the building, also have a significant impact on the temperature inside. Large windows on the south side bring a lot of sunlight into the interior, which significantly reduces the need for energy to heat the house in winter.
Summary
Energy-efficient and passive houses are the future of sustainable construction. They not only minimize the negative impact on the environment, but also offer residents comfort and significant financial savings. Investing in technologies such as energy-saving joinery, appropriate insulation or solar energy systems is a step towards a greener and more economical future.